In recent years, manufacturing technology has become faster, more affordable and more effective than ever. Read on to find out how rapid prototyping – using either 3D printing or CNC machining services – is transforming the way modern engineers work. Find more detailed information in our CNC machining design guide.
While traditional prototyping methods require engineers to manually craft every part they produce, modern manufacturing technologies allow today’s engineers to save time and money on sourcing and fabricating prototypes – while yielding far better results!
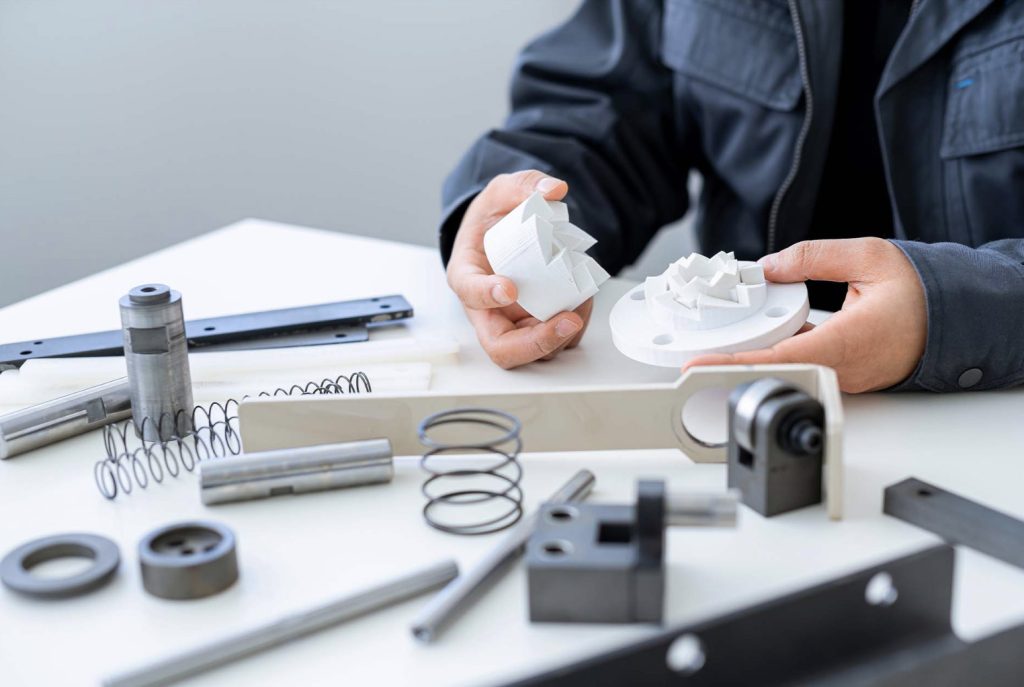

Today, we’re breaking down what rapid prototyping is, the two most popular rapid prototyping methods and how this fast new form of fabrication is transforming the engineering world.
What is rapid prototyping?
Coined in the 1970s, rapid prototyping is a relatively new term which essentially describes the process of creating prototypes quickly to visually and functionally evaluate an engineering product design.

These prototypes can be created using additive manufacturing (more commonly known as 3D printing) or subtractive manufacturing (for example, using CNC machining services) – and we’ll get into the differences between these two approaches shortly. In terms of where rapid prototyping is used, the method is commonly applied in software engineering to try out exciting new business models and application architectures – from the aerospace and automotive industries to product development and healthcare.
Fun fact: Rapid prototyping using 3D production systems has even allowed electric cars to be built and tested in a year!
SMARTER, FASTER, BETTER
RAPID PROTOTYPING IN THE MODERN DAY
What are the benefits of rapid prototyping?
At Dai Phong, we believe that rapid prototyping has essentially nothing but upsides! Whether you’re looking to save time, money or create more accurate prototypes, rapid prototyping is your friend. Here are just a few major advantages of using modern manufacturing technology to level up your engineering game:
It’s fast
Perhaps the biggest benefit of rapid prototyping is that it helps engineers reduce product development time significantly. The time it takes to create a part can vary from a few days to a number of months, depending on the project and on the methods used, but it’s almost always faster than using more traditional methods to create your prototypes.
It’s cost-effective
Rapid prototyping is an affordable and cost-effective way to create high-quality prototypes because it is, above all, an automated process. The process requires less staff to work on projects manually, as 3D printers and CNC machines can take care of most of the work – and, unlike people, can run for hours, days and even months without any breaks!
It’s extremely precise
There is generally far less room for error in rapid prototyping, as manufacturers are able to use computer aided design (CAD) to quickly review the details of every file, reduce material wastage and get each prototype right the first time, every time.
Of course, there is also far less room for human error when you leave it to the machines to do what they do best.
It allows for more flexibility in the design process
Rapid prototyping allows you to gain a more complete picture of how a product will look or perform in the early stage of the design and manufacturing cycle, allowing changes or improvements to be implemented far earlier in the process. As rapid prototyping is an iterative process, it also allows customer requirements to be incorporated into designs cost-effectively. Now that we’ve covered some of the key benefits of rapid prototyping, let’s take a look at two of the most popular ways of going about it:
Using 3D printing (additive manufacturing) for rapid prototyping
Additive manufacturing (more commonly known as 3D printing) is a process whereby three dimensional objects are created layer-by-layer using 3D object scanners or CAD (computer aided design). 3D printing uses materials such as plastic filaments (FDM), resins (SLA/DLP), plastic or metal powders (SLS/DMLS/SLM) to create each part.
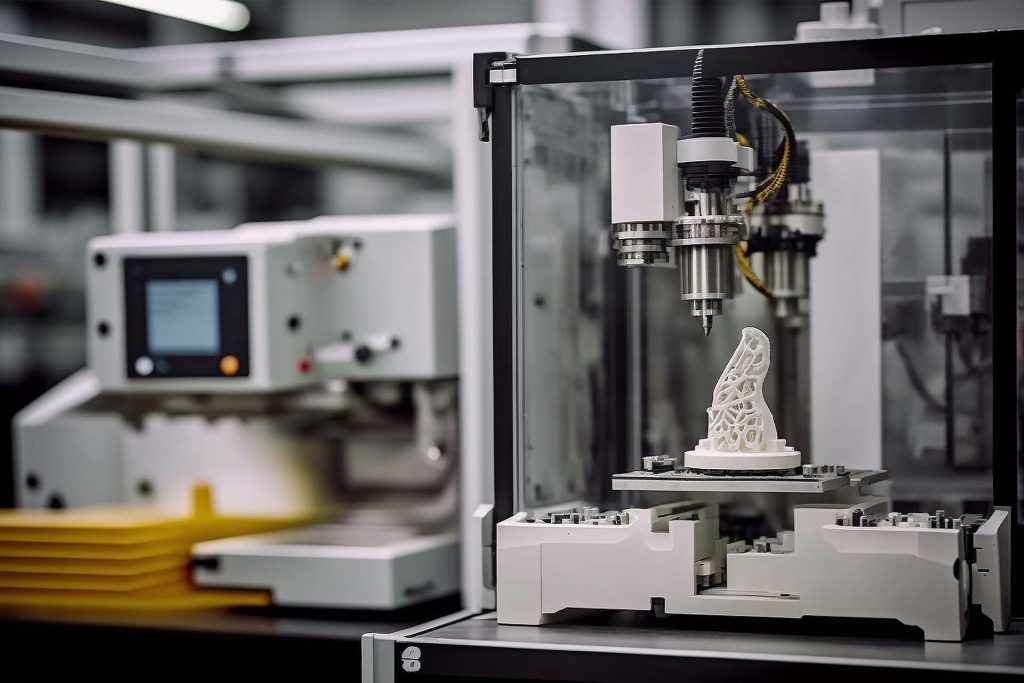

There are a few reasons why engineers might choose 3D printing (additive manufacturing) over CNC machining (subtractive manufacturing). For example:
It’s cheaper to create low volumes of parts
If you’re looking to create 80 or less parts or prototypes, 3D printing tends to be slightly cheaper on average.
3D printing reduces waste and is more environmentally friendly
Since additive manufacturing forms an object on the build platform from material fed into the machine, there is far less unused waste than in CNC machining (which involves cutting material away from an original block). This makes 3D printing the more ethical of the two methods – as it’s far kinder to our planet!
It’s super speedy
3D printing is generally the more appropriate choice if you need your prototypes or parts made very quickly.
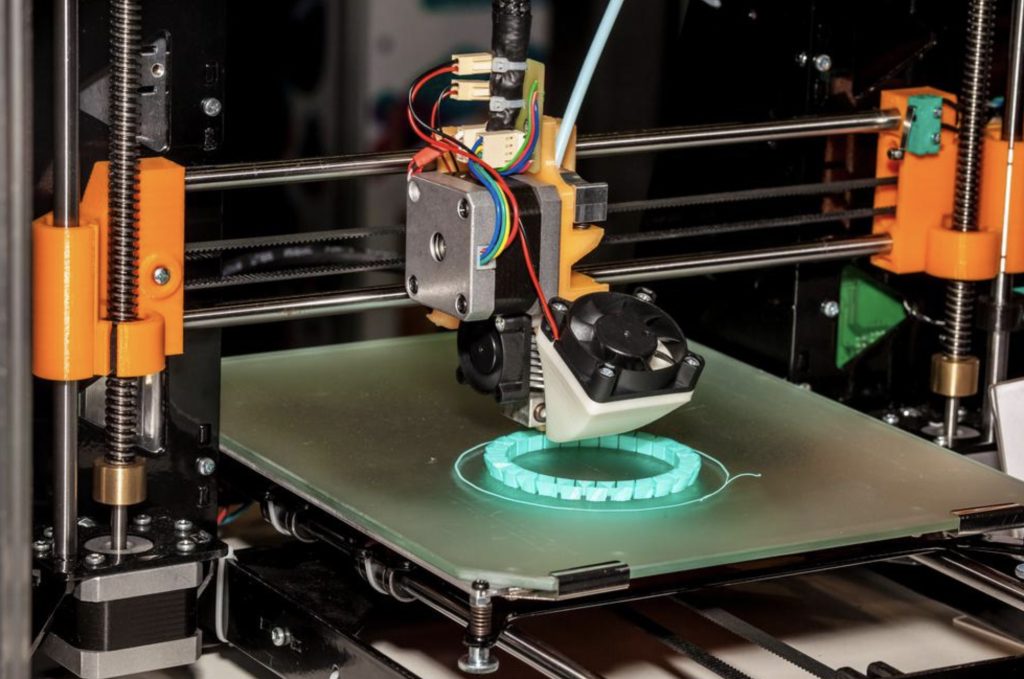
3D printers can handle higher levels of geometric complexity
While supports may be required for some projects, 3D printing is well-known and loved for being able to create parts with geometries that no traditional manufacturing method can replicate.It’s worth noting that 3D printing does tend to be the most popular method for rapid prototyping (you can find more information about 3D printing in our 3D printing design guide).
However, rapid prototyping is absolutely not a one-size-fits-all process, and it’s important to consider other options too:
Using CNC machining (subtractive manufacturing) for rapid prototyping
The key difference between 3D printing and CNC machining is that while 3D printing is a form of additive manufacturing, CNC machining is subtractivesubtractive. This means CNC machining starts with a block of material (called a blank), and uses fast-moving cutters to quickly carve away material and create the finished part. Some advantages of CNC machining include:
It’s cheaper to create large quantities of prototypes and parts
For larger quantities of mechanical parts (from the higher double digits into the 100s) CNC is likely to be a more cost-effective choice, compared to 3D printing.
CNC machines can work with more materials
While 3D printing is largely focussed on plastics, CNC machines are relatively indifferent to what they are cutting – so long as the material is rigid enough not to deform or melt under the pressure of the cutting action. Commonly used metals include aluminium, stainless steel, magnesium alloy, zinc alloy, titanium and brass.
Should you choose 3D printing or CNC machining services when creating prototypes?
While both 3D printing and CNC machining methods are extremely effective, the most appropriate one for your project will depend on the material you’re looking to use, the geometric complexity of your project, the manufacturing volume and – of course – your budget.
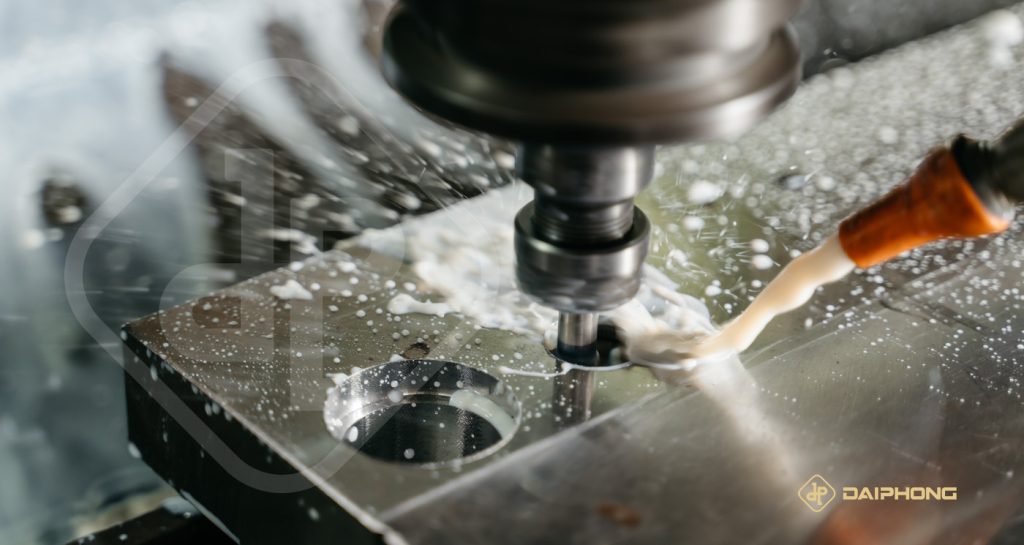

For example, if you’re looking to create a low volume of affordable prototypes, 3D printing is probably your best bet, whereas if you are looking to create higher quantities of parts (100+), CNC is likely to be your most cost-effective option.
To find out which method is right for you and your project’s unique requirements, we’d advise you to speak to a trustworthy manufacturing platform or provider and ask for their advice. Rapid prototyping technologies allow engineers to work faster, smarter, better and more flexibly. Plus, with online platforms like ours allowing you to source these expert services both locally and globally, the right rapid prototyping is only ever a few clicks away.
Soure from Internet


